Using Curcumin Nanoparticles to Enhance Cognition and Neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease
Around 1.5 billion of the world’s population are being affected by neurodegenerative disorders.[12] Neuroinflammation is the principal contributor to neurodegeneration by breaking down the selectivity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), causing morphological changes due to tissue damage by the infiltrating leukocytes.[12] Leukocytes are the so-called white blood cells produced by the body for protection against diseases.[2,12] However, the abnormal accumulation of misfolding proteins like the amyloid beta in the case of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) activates the neuroinflammation response, participating in several cells from the immune system, including the infiltrating leukocytes.2,12] The BBB generally restricts normal leukocytes. However, several investigations have shown that many neurodegenerative disorders cause the infiltration of white blood cells in the brain.[1]
On the other hand, some articles demonstrated that the overexpression of some inflammatory mediators in the brain (IL-1B, IL-6, IL-23, TNF-alpha) is responsible for neuronal death and damage.[12] For combating neuroinflammation, the body has a mechanism called “heat shock response,” which helps in giving neuroprotection against inflammation, high temperature, and infections, among other stressors.[12] In general, the genes that encode the heat shock response are called vitagenes.[12] Vitagenes helps in the assembly of antioxidant and the initiation of cell pro-survival pathways.[3,12] Recent studies have identified the expression of the vitagenes for combating the toxicity caused by the abnormal aggregation of proteins like the amyloid beta or the tau protein in AD models.[1,3,6,12]
The complexity behind AD lies in several outcomes mainly caused by the increased levels of misfolding proteins. Usually, AD models present some pathological features like poor homeostasis capacity, high neuron mortality, abnormal oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and dysfunction of the CNS.[4] Different investigations have shown that these pathological features affect the integrity of the proteins that compose the brain, including the vitagenes, thus impacting the lifespan, aging regulation, and health of the individual.[5,7] Several in vivo studies suggest that polyphenols increase the activity of the heat shock response, principally by stimulating the heat shock protein called (Hsp) and other proteins from the (Hsp) family.[8,9,12] Boosting the Hsp family is crucial in combating the pathological features of AD.[12] Recently, investigators suggested the use of hydrophobic polyphenol curcumin for treating AD and other neurodegenerative disorders since this molecule has pharmacological properties.[1-5] Curcumin can decrease neuroinflammation, anticancer, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, increase neuroprotection and anti-amyloid characteristics.10,11,13] The curcumin reduces neuroinflammation by downregulating several cytokines.[3,8,13]
However, some articles suggest that curcumin has low bioavailability and drug delivery. [3,5] To overcome this limitation, some investigators propose using a nano-based curcumin delivery system called PLGA-based curcumin (see Fig. 1). [5,6,9] Curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles have been shown to have enhanced bioavailability and improved drug delivery to the brain, making them a promising strategy for treating neurodegenerative disorders such as AD. [8,13] Recent studies have shown that curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles have the potential to inhibit the formation of the amyloid beta and the tau proteins in the brain, which are hallmarks of AD.[1,10] This new therapy also helps reduce oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, which contribute to neurodegeneration.[1-7] Several articles suggest that this therapy can improve memory and cognitive function in different AD models.[12] PLGA-based curcumin also promotes the proliferation, neuronal differentiation, and self-renewal of nervous system cells, helping repair the damage caused by neurodegeneration (see Fig.3).[11]
Nano-based curcumin delivery system for targeted delivery and improvement of water solubility and bioavailability of curcumin.[12]
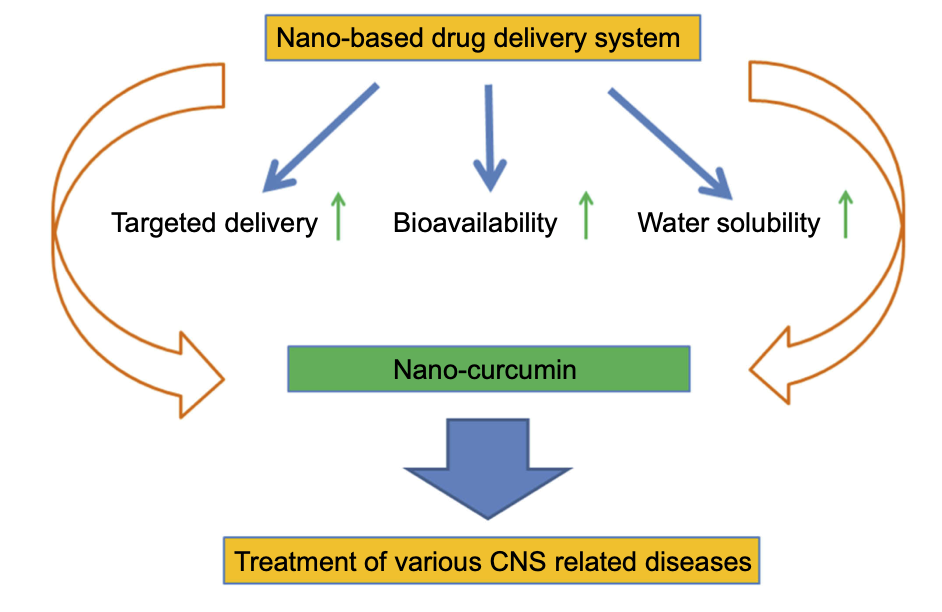
Figure 1.
The PLGA-based curcumin treatment for AD uses nanoparticles to transport curcumin to the brain. [1-3] The nanoparticles comprise PLGA, a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer.[5] The nanoparticles are small enough to cross the BBB, which is typically challenging for medications targeting the brain.[5] Once the nanoparticles reach the brain, they release curcumin, reducing neuroinflammation, inhibiting the aggregation of misfolding proteins, and improving neuroprotection and cognition.[1-5] In other words, by decreasing neuroinflammation and inhibiting the development of abnormal proteins, PLGA-based curcumin remedy can slow down or even reverse the advancement of AD.[5-9 Several articles have shown that the PLGA-based curcumin treatment can help in combating other neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s disease (PD) by reducing PD symptoms, apoptosis, and oxidative stress.[12] The PLGA-based curcumin therapy could provide a wide range of benefits in AD patients by decreasing the progression of most of the pathological aspects of the disorder.[5-10] In addition, this therapy overcomes one of the most challenging aspects of AD treatment, which is to cross the BBB.[1] PLGA-based curcumin provides a safe, viable, stable, nontoxic, and efficient way to fight AD progression.[11] Clinical trials for PLGA-based curcumin are ongoing, aiming to study the effectiveness and safety of using this treatment on humans.[10-13] Even though the results are unavailable, the preclinical studies show remarkable results in mice models.[12]
Benefit summary of the nano-based curcumin delivery system (PLGA-based curcumin)
- Decrease Amyloid beta and tau misfolding, accumulation, and toxicity.
- Improves memory and cognition in AD models (see Fig. 2).
- High circulation time in blood and bioavailability
- Cross the Blood-brain barrier
- Decreases neuronal cell death.
- Reduces neuroinflammation dramatically.
- Enhances neuroprotection and neuroplasticity.
- Inhibit the activation of cytokines.
- Promotes the heat shock response.
- Reduces the immune cell infiltration.
Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles significantly reversed the Aβ-induced deficits in learning and memory compared to control rats.[11]

Figure 2.
References
- Barbara, R., Belletti, D., Pederzoli, F., Masoni, M., Keller, J., Ballestrazzi, A., … & Grabrucker, A. M. (2017). Novel Curcumin loaded nanoparticles engineered for Blood-Brain Barrier crossing and able to disrupt Abeta aggregates. International journal of pharmaceutics, 526(1-2), 413-424.
- Djiokeng Paka, G., Doggui, S., Zaghmi, A., Safar, R., Dao, L., Reisch, A., … & Ramassamy, C. (2016). Neuronal uptake and neuroprotective properties of curcumin-loaded nanoparticles on SK-N-SH cell line: role of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) polymeric matrix composition. Molecular pharmaceutics, 13(2), 391-403.
- Ege, D. (2021). Action mechanisms of curcumin in Alzheimer’s disease and its brain targeted delivery. Materials, 14(12), 3332.
- Huang, N., Lu, S., Liu, X. G., Zhu, J., Wang, Y. J., & Liu, R. T. (2017). PLGA nanoparticles modified with a BBB-penetrating peptide co-delivering Aβ generation inhibitor and curcumin attenuate memory deficits and neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Oncotarget, 8(46), 81001.
- Lin, Y. W., Fang, C. H., Yang, C. Y., Liang, Y. J., & Lin, F. H. (2022). Investigating a curcumin-Loaded PLGA-PEG-PLGA thermo-sensitive hydrogel for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants, 11(4), 727.
- Mathew, A., Fukuda, T., Nagaoka, Y., Hasumura, T., Morimoto, H., Yoshida, Y., … & Kumar, D. S. (2012). Curcumin loaded-PLGA nanoparticles conjugated with Tet-1 peptide for potential use in Alzheimer’s disease.PLoS one, 7(3), e32616.
- Neurogenesis, P. I. A. Curcumin-Loaded Nanoparticles.
- Ray, B., Bisht, S., Maitra, A., Maitra, A., & Lahiri, D. K. (2011). Neuroprotective and neurorescue effects of a novel polymeric nanoparticle formulation of curcumin (NanoCurc™) in the neuronal cell culture and animal model: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease, 23(1), 61.
- Shabbir, U., Rubab, M., Tyagi, A., & Oh, D. H. (2020). Curcumin and its derivatives as theranostic agents in Alzheimer’s disease: The implication of nanotechnology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 196.
- Shahbaz, S. K., Koushki, K., Sathyapalan, T., Majeed, M., & Sahebkar, A. (2022). PLGA-based curcumin delivery system: An interesting therapeutic approach in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Current Neuropharmacology, 20(2), 309.
- Tiwari, S. K., Agarwal, S., Seth, B., Yadav, A., Nair, S., Bhatnagar, P., … & Gupta, K. C. (2014). Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles potently induce adult neurogenesis and reverse cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model via canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. ACS nano, 8(1), 76-103.
- Yavarpour-Bali, H., Ghasemi-Kasman, M., & Pirzadeh, M. (2019). Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic strategy in treatment of central nervous system disorders. International journal of nanomedicine, 4449-4460.
- Zeng, H., Xu, L., Zou, Y., & Wang, S. (2023). The impacts of curcumin on learning memory function in Alzheimer’s disease under the poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticle drug carrier. Applied Nanoscience, 13(5), 3483-3491.
Appendix
Figure 3. Comparison of uncoated bulk curcumin (BC) with the curcumin-loaded nanoparticles (Cur-PLGA-NPs) performance in the brain. Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles increase cell proliferation. This comparison was studied by measuring neurospheres, a culture system of free-floating clusters of neural stem cells.[11]
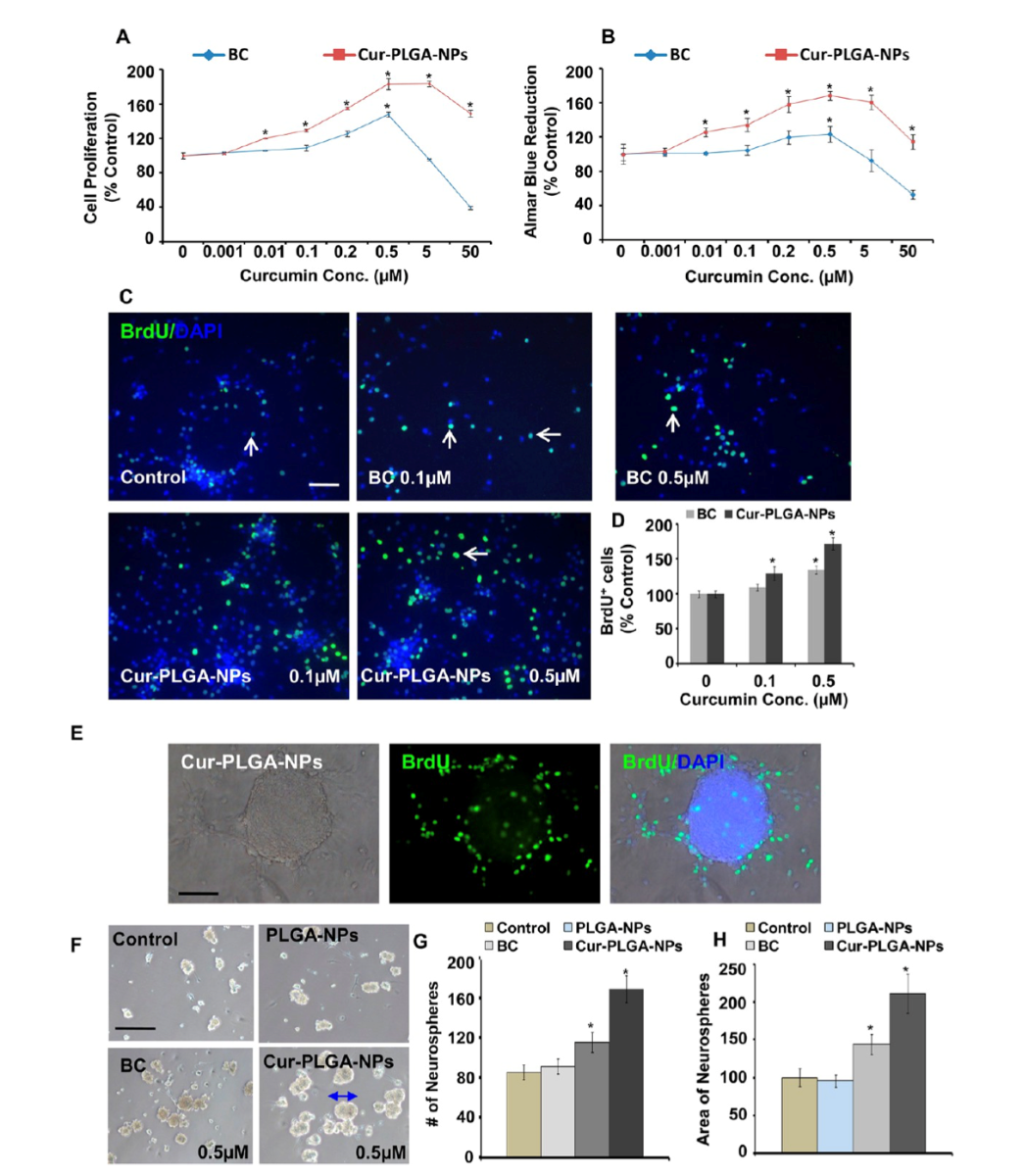
Figure 4. Findings of the effect of the curcumin-loaded nanoparticles in AD and other neurodegenerative disorders (Parkinson’s disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Huntington’s disease, and Epilepsy).[12]

